What Is Budgeting? A Comprehensive Guide to Financial Planning

What is budgeting? At its core, budgeting is creating a plan to manage your income, expenses, and financial goals. It involves outlining how much money you earn, how you intend to spend it, and how you plan to save or invest for the future. Budgeting is essential for achieving short-term objectives, like paying off debt, and long-term aspirations, such as buying a home or retiring comfortably.
What is budgeting?
Budgeting is the practice of allocating your income toward various expenses, savings, and debt repayments. It serves as a roadmap for your financial journey, helping you make informed decisions about spending and saving.
Why is budgeting important?
- Financial Control: Budgeting empowers you to take control of your finances by providing a clear picture of your income and expenditures. It allows you to monitor where your money is going, identify unnecessary expenses, and make adjustments to align your spending with your financial priorities. This control helps prevent overspending and ensures that your financial resources are used effectively.
- Goal Achievement: By setting clear financial goals and tracking your progress, budgeting helps you achieve milestones like purchasing a car, saving for a vacation, or building an emergency fund. It enables you to allocate funds toward specific objectives, making it easier to plan for both short-term desires and long-term aspirations. Regularly reviewing your budget keeps you focused and motivated to reach these goals.
- Debt Management: A well-structured budget allows you to allocate funds toward paying off debts systematically, reducing financial stress. By prioritizing debt repayment within your budget, you can create a clear plan to eliminate liabilities, avoid accumulating additional debt, and improve your overall financial health. This proactive approach to managing debt contributes to long-term financial stability.
Types of Budgets
What is budgeting in types of budgeting?
Budgeting can be categorized into various types, each serving different purposes:
Static Budget
A static budget is a financial plan that remains unchanged throughout a specific period, regardless of variations in business activity levels. It’s commonly used by organizations with predictable financial patterns. Vena Solutions
Key Characteristics:
- Fixed Estimates: Static budgets are based on anticipated values about inputs and outputs conceived before the period begins. Vena Solutions
- Performance Benchmarking: They serve as a benchmark for evaluating actual performance, helping organizations assess how well they adhere to their financial plans. Brixx
Example:
Consider a company that sets a static budget allocating $50,000 for marketing expenses for the year. Even if the company’s sales increase or decrease, the marketing budget remains at $50,000. AccountingTools Investopedia
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Easy to prepare and implement, making it suitable for organizations with stable operations. Brixx
- Cost Control: Helps in maintaining strict control over expenditures.
Limitations:
- Inflexibility: Does not accommodate changes in business activity, which can lead to variances between budgeted and actual figures. Vena Solutions
- Less Responsive: May not be suitable for dynamic business environments where adaptability is crucial.
Flexible Budget
A flexible budget adjusts based on changes in income or business activity levels. It’s particularly useful for businesses with fluctuating revenues.
Key Characteristics:
- Adaptability: Adjusts to changes in activity levels, providing a more accurate reflection of costs and revenues. Accounting Coach
- Enhanced Performance Evaluation: Allows for better analysis of variances by comparing actual results to budgeted figures adjusted for actual activity levels. Datarails
Example:
A restaurant anticipates serving 2,000 customers in a month, budgeting $10,000 for food supplies. If the actual number of customers increases to 2,500, the flexible budget adjusts the food supplies budget proportionally to $12,500.
Advantages:
- Realistic Planning: Provides a more accurate picture of financial performance by accounting for actual activity levels. Datarails
- Better Control: Helps in managing costs effectively by adjusting budgets in response to changes in business conditions.
Limitations:
- Complexity: Requires more detailed analysis and frequent updates, which can be time-consuming.
- Data Dependency: Relies heavily on accurate and timely data to make appropriate adjustments.
Personal Budget
A personal budget is tailored to an individual’s or family’s income and expenses, focusing on managing daily finances and achieving personal financial goals.
Key Characteristics:
- Income Allocation: Involves planning how to allocate income towards expenses, savings, and debt repayments.
- Financial Goal Setting: Helps in setting and tracking progress towards financial goals like buying a house, saving for education, or retirement planning.
Example:
An individual earns PKR 100,000 per month and allocates 50% for necessities (rent, utilities), 30% for wants (entertainment, dining out), and 20% for savings and debt repayment. This follows the 50/30/20 budgeting rule.
Advantages:
- Financial Awareness: Enhances understanding of spending habits and areas where adjustments can be made.
- Debt Management: Assists in planning debt repayments, reducing financial stress.
Limitations:
- Discipline Required: Requires consistent tracking and discipline to adhere to the budget.
- Unexpected Expenses: May need adjustments to accommodate unforeseen expenses or changes in income.
Popular Budgeting Methods
What is budgeting through different methods?
Several budgeting methods can help individuals manage their finances effectively:
50/30/20 Budget:
This method divides after-tax income into three categories: Budgeting Now
- 50% Needs: Essential expenses like housing, utilities, and groceries. NYSUT
- 30% Wants: Non-essential items such as dining out and entertainment.
- 20% Savings: Savings and debt repayment. Ramp
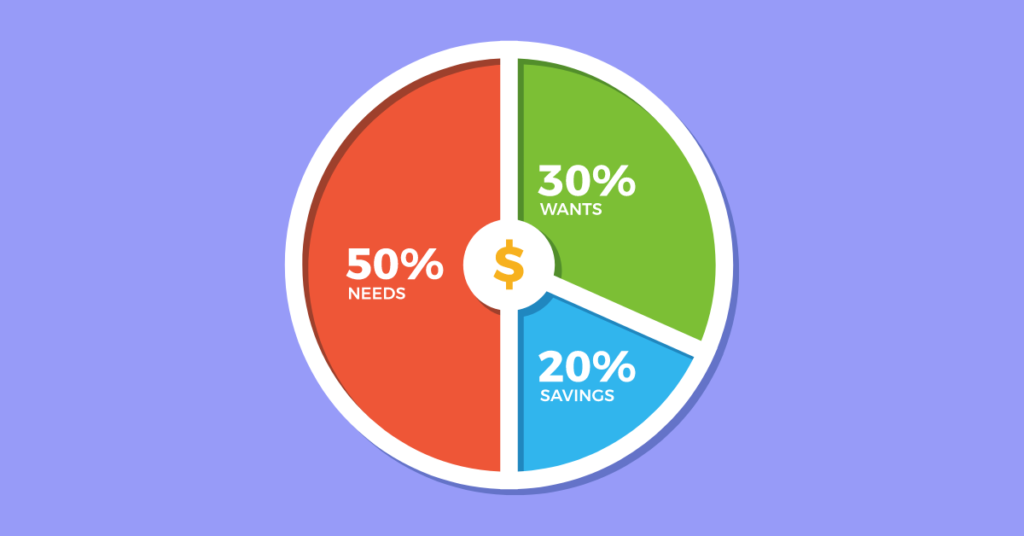
60/30/10 Budget:
An alternative approach to allocating:
- 60% Needs: Basic living expenses. Accredited Debt Relief
- 30% Wants: Discretionary spending. Magnify Money
- 10% Savings: Savings and debt reduction. Member Benefits
Steps to Create a Personal Budget
What is budgeting in practice?
Budgeting in practice involves a systematic approach to managing your finances by tracking income, expenses, and setting financial goals. It’s a dynamic process that requires regular monitoring and adjustments to ensure financial stability and goal achievement.
Outline Your Income
Begin by calculating your total monthly income from all sources, including salary, freelance work, investments, or any other earnings. Understanding your income is crucial as it sets the foundation for your budgeting plan. Ensure to consider your net income (after taxes and deductions) for accurate budgeting.
Track Expenses
Monitor your spending to understand where your money goes. Categorize your expenses into fixed (rent, utilities) and variable (groceries, entertainment) costs. Utilize tools like budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or financial journals to record your expenses diligently. This practice helps identify spending patterns and areas where you can cut back. WAEPA
Review Account Balances and Debts
Assess your current financial standing by reviewing your bank account balances, outstanding debts, and credit card statements. Understanding your liabilities and assets provides a clear picture of your financial health and informs your budgeting decisions.
Review Your Spending
Analyze your tracked expenses to identify areas where you can reduce spending. Look for non-essential expenditures that can be minimized or eliminated. This step is vital in reallocating funds towards savings or debt repayment.
Create a Spending Plan
Develop a spending plan by allocating funds to various categories based on your priorities and financial goals. Ensure that essential expenses are covered, and set aside amounts for savings and discretionary spending. This plan serves as a roadmap for your financial activities.
Set Financial Goals
Define your short-term and long-term financial objectives, such as building an emergency fund, saving for a vacation, or planning for retirement. Setting clear goals provides motivation and direction for your budgeting efforts.
Adjust Each Month
Regularly review and modify your budget to reflect changes in income, expenses, or financial goals. Life circumstances can change, and your budget should be flexible enough to accommodate these changes. Consistent adjustments ensure that your budget remains effective and aligned with your financial objectives.
Importance of Budgeting
What is budgeting’s role in financial well-being?
Budgeting serves as a foundational tool for achieving financial stability and peace of mind. By providing a structured approach to managing income and expenses, budgeting empowers individuals to make informed financial decisions. Let’s explore the key benefits:
Awareness: Understanding Your Spending Habits
Budgeting enhances your awareness of where your money goes. By tracking expenses, you can identify spending patterns, distinguish between needs and wants, and recognize areas where you might be overspending. This insight is crucial for making adjustments that align with your financial goals.
Planning: Preparing for Upcoming Expenses
A well-structured budget allows you to anticipate and plan for future expenses, both expected and unexpected. Whether it’s saving for a vacation, preparing for seasonal bills, or setting aside funds for emergencies, budgeting ensures you’re financially prepared. Lending Club
Saving: Allocating Funds for Future Needs
Budgeting facilitates intentional saving by allocating a portion of your income toward future needs. This could include building an emergency fund, saving for retirement, or investing in personal development. Consistent saving through budgeting helps in accumulating wealth over time.
Debt Reduction: Systematically Paying Off Debts
By incorporating debt repayment into your budget, you can systematically reduce and eventually eliminate debts. Budgeting helps prioritize high-interest debts, allocate extra funds toward repayments, and track progress, leading to improved financial health.
Stress Relief: Reducing Financial Anxiety Through Organized Planning
Financial uncertainty can be a significant source of stress. Budgeting brings structure and clarity to your finances, reducing anxiety by providing a clear plan for managing income and expenses. Knowing you have a plan in place offers peace of mind and confidence in your financial decisions.
Common Budgeting Myths
What is budgeting often misunderstood as?
Several misconceptions can deter individuals from budgeting:
- “I Don’t Need to Budget”: Everyone can benefit from financial planning.
- “I’m Not Great at Math”: Budgeting tools simplify calculations.
- “My Job Is Secure”: Unexpected events can impact income.
- “I Don’t Want to Deprive Myself”: Budgeting allows for controlled spending on wants.
- “I’m Debt-Free”: Budgeting helps maintain financial health.
Budgeting Tools and Resources
What is budgeting facilitated by?
Utilize various tools to streamline budgeting:
- Budgeting Apps: Applications like Mint or YNAB help track expenses.
- Spreadsheets: Customizable templates for detailed planning.
- Financial Advisors: Professional guidance for complex financial situations. Budgeting Now
Corporate Budgeting
What is budgeting in a business context?
Businesses rely on budgeting for operational efficiency: Investopedia
- Sales Budget: Forecasts future sales to guide production and expenses.
- Operating Budget: Covers day-to-day expenses.
- Capital Budget: Plans for long-term investments.
Adjusting Your Budget
What is budgeting’s adaptability?
Budgeting is not a static process; it’s a dynamic tool that should evolve with your life’s changes. Whether it’s a shift in income, unexpected expenses, or changing financial goals, your budget should be flexible enough to accommodate these variations. Here’s how to adapt your budget effectively:
Income Changes: Adjust Spending and Savings Accordingly
Life events such as job changes, salary adjustments, or additional income sources can significantly impact your financial landscape. When your income increases, consider allocating extra funds toward savings, investments, or paying down debt. Conversely, if your income decreases, it’s crucial to reassess and reduce discretionary spending to maintain financial stability. Regularly reviewing and updating your budget ensures it aligns with your current income levels.
Unexpected Expenses: Reallocate Funds to Cover Emergencies
Emergencies like medical bills, car repairs, or urgent home maintenance can disrupt your financial plans. To mitigate the impact, establish an emergency fund by setting aside a portion of your income regularly. This fund acts as a financial buffer, allowing you to cover unforeseen expenses without derailing your budget. Additionally, consider creating a “miscellaneous” category in your budget to handle minor unexpected costs. Money Fit
Goal Reassessment: Modify Objectives as Priorities Shift
Your financial goals may evolve due to life changes such as marriage, parenthood, or career shifts. It’s essential to revisit and adjust your budget to reflect these new priorities. For instance, if you’re planning to buy a home, you might need to increase your savings allocation. Regularly evaluating and realigning your budget with your current goals ensures you stay on track toward achieving them.
Conclusion
What is budgeting? It’s a fundamental tool for managing your finances, achieving goals, and securing your financial future. By understanding and implementing effective budgeting strategies, you can take control of your money and make informed financial decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Q1. What is the simple definition of budgeting?
Budgeting is the process of calculating how much money you must earn or save during a particular period of time, and planning how you will spend it.
Q2. What is the main purpose of budgeting?
The primary purpose of budgeting is to keep track of the money you are earning and spending, ensuring that your expenses align with your income.
Q3. Why is budgeting necessary?
Budgeting is essential because it helps create financial stability by allowing you to plan for expenses, save for future goals, and avoid unnecessary debt.
Q4. What is the principle of budgeting?
The core principle of budgeting is setting clear financial goals and targets, enabling you to allocate resources effectively to meet those objectives.
Q5. What are the 5 benefits of budgeting?
- Prevents Overspending: Keeps your expenses within your income limits.
- Manages Debt: Helps in systematically paying off debts.
- Achieves Goals: Guides you toward short- and long-term financial objectives.
- Prepares for Emergencies: Allocates funds for unexpected expenses.
- Simplifies Saving: Makes saving for retirement and other goals more manageable.
Q6. Which budgeting method is best?
The best budgeting method depends on individual financial situations:
- Zero-Based Budget: Ideal for tracking consistent income and expenses.
- Pay-Yourself-First Budget: Prioritizes savings and debt repayment.
- Envelope System Budget: Encourages disciplined spending.
- 50/30/20 Budget: Balances needs, wants, and savings effectively.








How to Make Money Online Without Investment - 12 Smart Ways
17th May 2025[…] What Is Budgeting? A Comprehensive Guide to Financial Planning […]